Understanding Meniscus Tears
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/meniscusfinal-01-5c8fba21c9e77c00010e96f5.png)
Imagine your knee as a complex hinge that lets you bend, straighten, and twist. It’s made up of bones, ligaments, cartilage, and a crucial component called the meniscus. This C-shaped piece of rubbery cartilage acts like a shock absorber, cushioning your knee joint and distributing weight evenly. But what happens when this vital piece tears?
Anatomy of the Knee Joint
The knee joint is one of the largest and most complex joints in the body. It’s where the thighbone (femur) meets the shinbone (tibia) and kneecap (patella). The meniscus sits between these bones, acting as a buffer. It’s made of two parts: the medial meniscus (on the inner side of the knee) and the lateral meniscus (on the outer side).
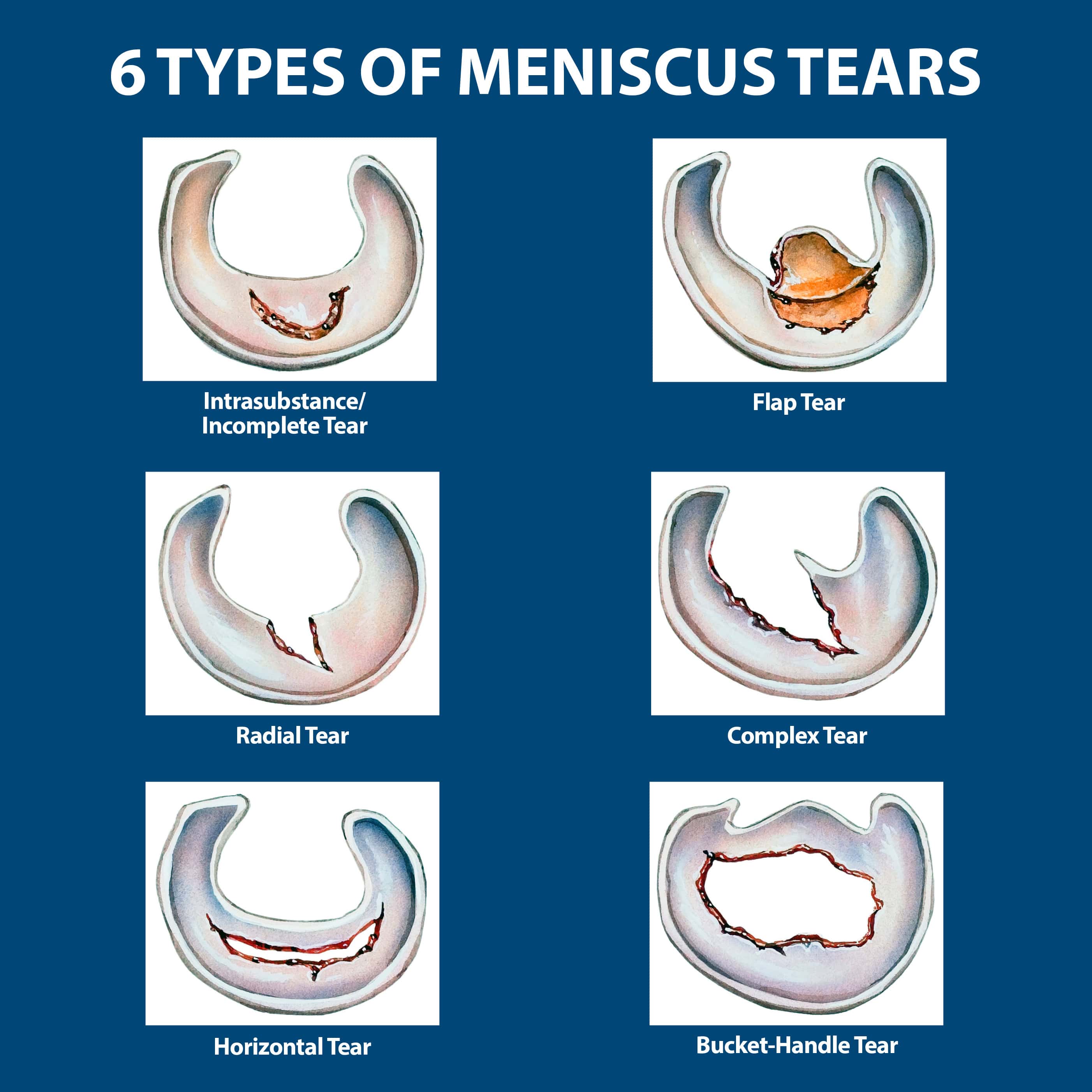
Types of Meniscus Tears
Meniscus tears can occur in various ways, depending on the type of injury. The most common types include:
Types of Meniscus Tears
- Horizontal tear: This tear runs across the meniscus, like a cut.
- Vertical tear: This tear runs up and down the meniscus, like a split.
- Radial tear: This tear looks like a spoke on a wheel, radiating from the center of the meniscus.
- Degenerative tear: This tear occurs over time due to wear and tear, often affecting older individuals.
Causes of Meniscus Tears
Meniscus tears are often caused by sudden twisting or pivoting movements, especially when the knee is bent.
Activities that can Lead to Meniscus Tears
- Sports: Football, basketball, skiing, and tennis are some sports that put stress on the knee joint.
- Accidents: A fall or direct blow to the knee can also cause a tear.
- Repetitive movements: Certain occupations that involve kneeling or squatting can increase the risk of a meniscus tear.
Symptoms of Meniscus Tears
The symptoms of a meniscus tear can vary depending on the severity of the tear.
Symptoms of Meniscus Tears
- Pain: You may experience a sharp, sudden pain in your knee at the time of the injury.
- Swelling: The knee may swell up within a few hours or days after the injury.
- Stiffness: You may have difficulty bending or straightening your knee.
- Clicking or popping: You may hear or feel a clicking or popping sensation in your knee when you move it.
- Locking: The knee may lock in a bent position, making it difficult to straighten.
- Giving way: Your knee may feel unstable and give way under your weight.
Complications of Untreated Meniscus Tears
Ignoring a meniscus tear can lead to several complications.
Complications of Untreated Meniscus Tears
- Further damage to the knee: A torn meniscus can put additional stress on other structures in the knee, leading to further injuries.
- Osteoarthritis: Untreated meniscus tears can lead to the development of osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease.
- Chronic pain and instability: A torn meniscus can cause chronic pain and instability in the knee, limiting your mobility.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
After understanding what a meniscus tear is, let’s dive into how doctors figure out if you’ve got one and what they can do to help you heal.
Physical Examination
A physical exam is the first step in diagnosing a meniscus tear. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, how the injury happened, and your medical history. They’ll also examine your knee, checking for pain, swelling, tenderness, and range of motion. They’ll test your knee’s stability by moving it in different directions and might check your reflexes.
Imaging Scans
If your doctor suspects a meniscus tear, they may order imaging tests to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the tear. These tests include:
- X-rays: While X-rays don’t directly show the meniscus, they can rule out other conditions like fractures. They can also help assess for joint space narrowing or bone spurs.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This is the gold standard for diagnosing meniscus tears. MRI provides detailed images of the soft tissues, including the meniscus, ligaments, and cartilage. It can show the location, size, and type of tear.
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows doctors to visualize the inside of the knee joint. It involves inserting a thin, telescope-like instrument called an arthroscope into the joint through a small incision. This procedure can be used to both diagnose and treat meniscus tears.
Treatment Options
Once a meniscus tear is diagnosed, the treatment plan will depend on factors like the severity of the tear, your age, activity level, and overall health.
Conservative Treatment
For minor tears or those that aren’t causing significant symptoms, conservative treatment is often the first line of approach. This may involve:
- RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation): This helps reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist can teach you exercises to strengthen the muscles around your knee and improve flexibility and range of motion.
- Bracing: A knee brace can provide support and stability to the joint.
Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatment fails to relieve symptoms or if the tear is severe, surgery may be necessary. The most common surgical procedure for meniscus tears is arthroscopy.
Arthroscopic Surgery
During arthroscopic surgery, the surgeon will make small incisions around the knee and insert an arthroscope to visualize the inside of the joint. Depending on the type of tear, the surgeon may:
- Repair the tear: This involves stitching the torn meniscus back together. Repair is typically possible for tears that are located in the outer portion of the meniscus, which has a better blood supply.
- Remove the torn portion: This is called a meniscectomy. It is often performed for tears that are located in the inner portion of the meniscus, which has a poor blood supply and is less likely to heal.
Rehabilitation Program
After meniscus tear surgery, a rehabilitation program is crucial for regaining full function and preventing future injuries. This program typically involves:
- Rest and protection: Initially, you’ll need to avoid activities that put stress on your knee.
- Ice therapy: Applying ice to the area can help reduce swelling and inflammation.
- Exercises: Your physical therapist will guide you through a series of exercises to strengthen the muscles around your knee, improve range of motion, and restore stability.
- Gradual return to activity: As your knee heals, you’ll gradually increase your activity level, starting with simple exercises and progressing to more demanding activities.
Living with a Meniscus Tear

Recovering from a meniscus tear can be a challenging journey, but with the right approach, you can regain your knee function and enjoy an active lifestyle. It’s crucial to understand that healing takes time, and patience is key. This section will explore strategies for managing pain, improving mobility, and promoting long-term recovery.
Managing Pain and Improving Mobility
Managing pain and improving mobility after a meniscus tear is crucial for a successful recovery. Here are some effective strategies:
- Rest and Ice: Initially, rest your knee and apply ice packs to reduce swelling and pain. Ice for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
- Pain Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger medications.
- Compression: Using a compression bandage or brace can help reduce swelling and provide support.
- Elevation: Keep your knee elevated above your heart whenever possible to reduce swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is essential for regaining strength, flexibility, and range of motion. Your therapist will guide you through exercises tailored to your specific needs.
The Importance of Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy plays a vital role in your recovery after a meniscus tear. It helps:
- Strengthen Muscles: Physical therapy exercises target the muscles surrounding your knee, improving strength and stability.
- Improve Range of Motion: Exercises help restore flexibility and range of motion in your knee joint.
- Restore Function: Physical therapy aims to help you regain the ability to perform daily activities without pain or limitations.
- Prevent Future Injuries: By strengthening your muscles and improving your overall knee health, physical therapy can help prevent further injuries.
Lifestyle Modifications for Long-Term Recovery
Making certain lifestyle modifications can help prevent further injury and promote long-term recovery:
- Weight Management: Excess weight puts extra stress on your knees. Losing even a small amount of weight can significantly reduce the strain on your joint.
- Proper Footwear: Wear supportive shoes that provide good arch support and cushioning. Avoid high heels or flat shoes that lack support.
- Ergonomics: Pay attention to your posture and ensure your workplace is ergonomically designed to minimize strain on your knees.
- Warm-Up and Cool-Down: Always warm up before exercising and cool down afterward to prepare your muscles and prevent injury.
- Avoid High-Impact Activities: Initially, avoid activities that put excessive stress on your knee, such as running, jumping, or heavy lifting. Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your activities as your knee heals.
Long-Term Outcomes of Treatment Options
The long-term outcomes of different treatment options for meniscus tears vary depending on the severity of the tear, the individual’s activity level, and other factors. Here is a table comparing the success rates, risks, and limitations of common treatment options:
| Treatment Option | Success Rate | Risks | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conservative Treatment (Physical Therapy, Medications) | High for minor tears | May not be effective for severe tears | May require a longer recovery time |
| Arthroscopic Surgery (Partial Meniscectomy) | Generally high for symptomatic tears | Risk of infection, complications, and long-term joint degeneration | May not be effective for all types of tears |
| Meniscus Repair | Good for certain types of tears | More complex surgery with a longer recovery time | Not always possible for all types of tears |
A meniscus tear, a painful reminder of the fragility of our bodies, can be a setback, but it’s not the end of the journey. Just like JJ McCarthy, who’s making waves in the jj mccarthy news , is facing his own challenges, a meniscus tear can be a chance to re-evaluate, rebuild, and come back stronger.
With dedication and the right support, you can overcome this hurdle and continue your own journey towards your goals.
A meniscus tear, a common sports injury, can be a frustrating setback, forcing athletes to navigate a path of recovery and rehabilitation. We’ve seen this firsthand with the jj mcarthy injury , a reminder that even the most talented athletes can face these challenges.
But with dedication and the right support, athletes can overcome these obstacles and return to the field stronger than ever, demonstrating the resilience of the human spirit in the face of adversity.
